Heart Procedure Instructions
VARICOSE AND VEIN DISORDER SYMPTOM RECOGNITION. DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLAN
Venous disease is a progressive disorder, but its symptoms can be treated, and the progression of the disease can be halted by outpatient procedures.
Vein disease manifests as a cosmetic nuisance or can progress to significant skin changes, recurrent skin infections difficult to treat, skin ulcers, resulting in major increased morbidity and mortality
What is venous insufficiency
Leg veins contain one-way valves that allow blood to flow in one direction and return to the heart even against gravity. When the valves become incompetent and diseased or leak, blood pools in the leg veins, and the veins can become enlarged building pressure, visible under the skin , bulging , what we call varicose veins .
Symptoms can develop due to impaired blood flow in the affected veins before bulging varicosities appears. The sooner we diagnose and treat these veins after symptoms are present the better the outcomes are.
Symptoms of varicose veins and venous insufficiency
Painful Varicose veins
Recurrent swelling
Cramping, throbbing,
Heaviness
Fatigue
Night cramps
Itching
Restless legs
Numbness
Skin changes, hyperpigmentation, red dots, hypopigmentation, redness, induration
Recurrent skin infection, cellulitis
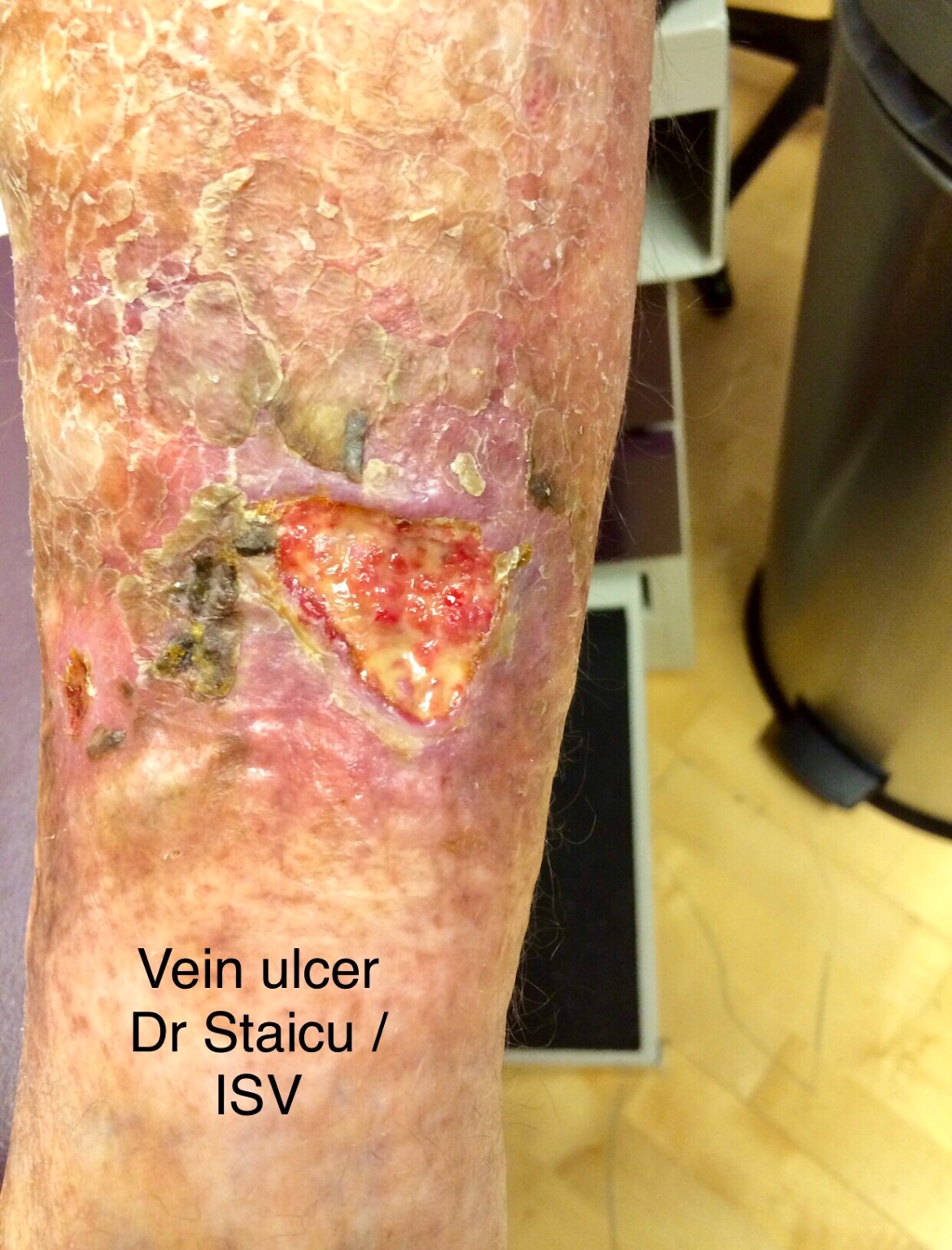
Skin breakdown and ulceration, non-healing ulcers
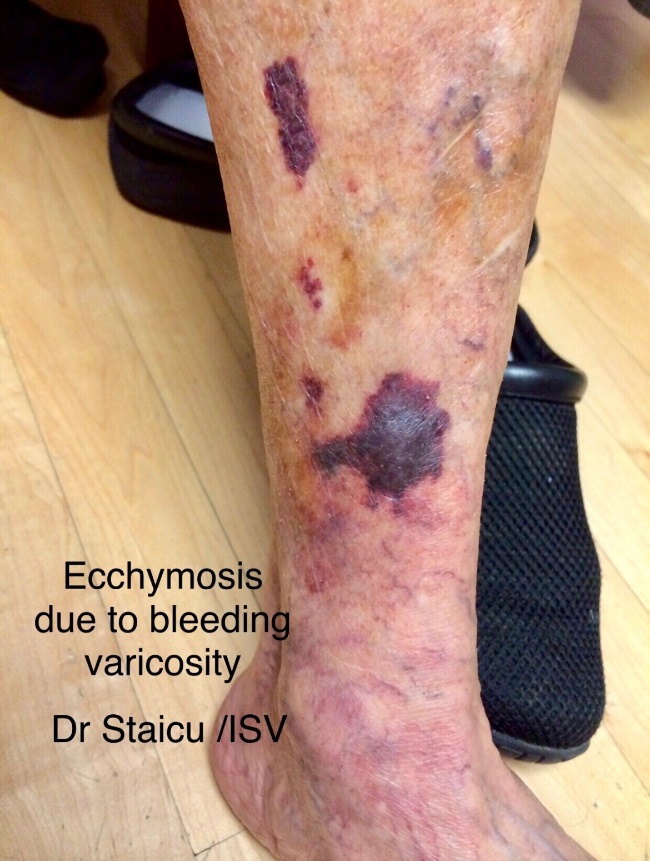
Bleeding of ruptured varicosities
Key points
Venous disease should not be defined as varicose veins only; venous disease means much more than varicose veins and the absence of varicose veins does not exclude venous disease. One may have significant venous disease by symptoms and ultrasound without bothersome visible varicose veins but with other clinical sequels of vein disease: recurrent skin infections, skin induration, hyper pigmentation, what we call venous stasis dermatitis. This form of vein disorder left untreated may progress to venous ulcer.
What you should expect on the first office visit
Physical examination and venous ultrasound are essential components of venous disease evaluation, together with the symptom recognition. These three components will play a role in deciding whether you need to proceed with medical therapy or you are a candidate for aggressive invasive treatment.
- At your first appointment you will be seen by a cardiovascular physician and a full history and physical evaluation will be performed.
- The first visit is followed by a venous duplex ultrasound to evaluate all veins in the leg and determine the status and the degree of diseased segment as well as the precise location and distribution of the affected veins.
- A treatment plan usually follows, which may be conservative- noninvasive or procedural – invasive depending on the degree and extend of your disease. The treatment plan, options, approach, procedure, will be discussed at the second visit, after reviewing the ultrasound
- You may be a candidate for medical therapy or invasive procedures
Treatment Options for Varicose Veins:
The goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and improve the appearance of the legs. There are several options available, including:
- Medical Therapy (Conservative Treatment):
- Compression Stockings: Wearing compression stockings (30-40 mm Hg) can improve blood flow and reduce symptoms like swelling and pain. They are especially recommended during the day.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding prolonged standing or sitting, elevating the legs, and exercising regularly can help reduce the progression of varicose veins.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures:
These outpatient treatments are highly effective in closing off varicose veins and redirecting blood flow to healthier veins. Benefits include minimal recovery time, no scars, and significant symptom relief.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Uses radio wave energy to heat and close off the affected vein. This redirects blood flow to healthier veins and relieves symptoms like pain and swelling.
- Laser Ablation: A laser is used to close off the diseased vein. This procedure is also non-invasive, with a high success rate and minimal discomfort.
- Sclerotherapy: Involves injecting a chemical solution into the varicose vein, causing it to collapse and fade over time.
What to Expect:
- These procedures are done under local anesthesia, are usually completed within an hour, and involve little to no downtime. Most patients return to normal activities the next day and report symptom improvement within a few days to weeks.
- Surgical Options (for Severe Cases):
In rare cases where varicose veins are advanced, surgery may be necessary to remove or close off the affected veins.
Patient Feedback After Varicose Vein Treatment:
Many patients report significant improvement in their symptoms and quality of life following treatment:
- “My vein ablation was easy and painless, and I felt much better within days.”
- “I was thrilled with the cosmetic results after my procedure, and my leg felt lighter almost immediately.”
- “If I had known how effective this treatment was, I would have done it much sooner.”
- “The procedure not only relieved my pain but also improved my ability to walk and be active.”
Benefits of Modern Varicose Vein Treatments:
- Non-surgical and outpatient procedures
- No scars and quick recovery times
- Improved appearance and symptom relief within days to weeks
- Reduced swelling and increased mobility
- Minimized downtime, allowing patients to return to normal activities the next day
These treatments are typically covered by insurance, especially if they are done to relieve symptoms rather than for cosmetic purposes.
Summary:
Varicose veins can be effectively treated with the latest minimally invasive procedures, improving both the appearance of your legs and your quality of life. With modern treatments such as radiofrequency ablation, laser ablation, sclerotherapy, and INSPIRE therapy, patients experience minimal discomfort, faster recovery, and excellent long-term results. Regular follow-ups and lifestyle adjustments can help prevent the recurrence of varicose veins and maintain better vascular health.
WHERE IS THE LINE BETWEEN COSMETIC AND MEDICAL VARICOSE VEIN DISEASE?
There is a difference in approaching and understanding varicose vein disease according to age.
Most of younger people approach vein disease with the desire to improve the aesthetic appearance and are surprised to learn that 75% of them already crossed the line of cosmetic to medical disease. Early vein disease symptoms are easily ignored: leg fatigue, fullness, cramping are vague and not specific to varicose disease. They come for cosmetic and uncover the medical depth of the disease
Older people present with different stages of medical vein disease, or with a complication, such as blood clots, recurrent cellulitis or leg infections. Initially they are not interested in cosmetic aspect, focusing on treating the serious complications of varicosities and reducing leg swelling or improving walking abilities. Venous medical treatment render significant relief of symptoms, changing the focus of treatment towards cosmetic.
” Since I feel much better why not wear shorts again” is one of the most common sentences heard after successful ablations. They present with a medical problem and after successful treatment, will ask for cosmetics
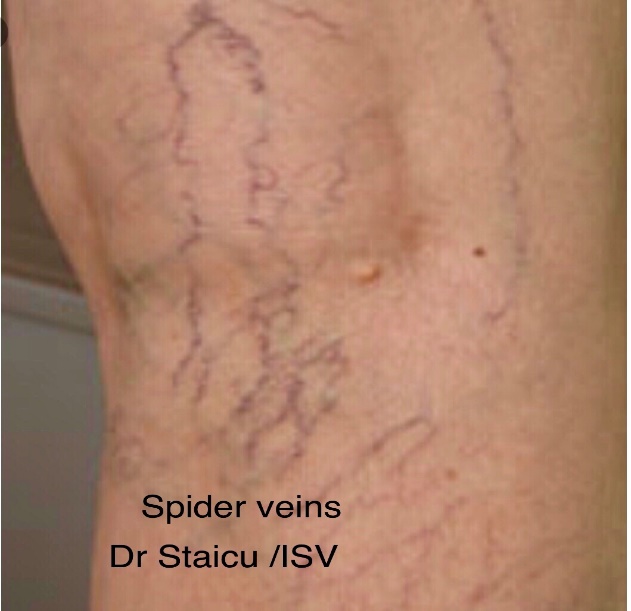
Spider veins are considered cosmetics, and not covered by insurances since are not associated with a medical condition.
Spider veins appear as tiny red or blue lines, usually less than 1 mm in diameter, that look like branches or a spider web just below the surface of your skin. You can see them but not feel them.
Spider veins may give pain, discomfort to touch , bleeding, however do not pose a serious medical threat .
Varicose veins are bulging, twisted blue blood vessels that can be seen and felt right under the surface of the skin. They are larger than spider and associated with symptoms as well as complications. The key difference is that varicose veins are seen and felt but spider are only seen, not palpable
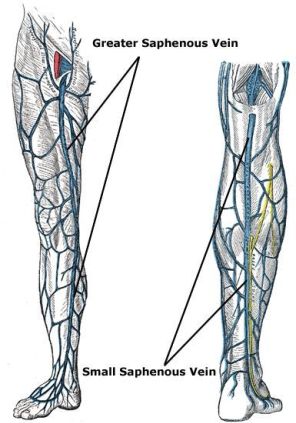
They are associated with abnormalities of larger superficial veins, saphenous veins, not seen with visible eye but with the ultrasound.
Medical symptoms and complications of varicose vein disease
- Recurrent edema, unresponsive to diuretics
- Stasis dermatitis, or skin changes, redness, induration, pigmentation, associated with pain, decrease mobility and prone to infections.
- Cellulitis, or skin infections, recurrent unless venous ablations are performed; they require hospitalization and weeks of antibiotics
- Skin ulceration, nonhealing, prone to infections
- Blood clots, called DVT, which is a serious medical condition with potentially fatal complications such as pulmonary embolism
- Thrombophlebitis when the superficial vein becomes painful, warm to the touch and hard.
- Bleeding from a visible varicosity when cut or hit triggering a significant amount of bleeding, hard to control. Or, if the skin isn’t broken, there may be large painful bruising
Spider veins – visible not palpable,cosmetic, not covered by insurance, not triggering serious medical complications,however, may be the early stage of venous disease.
Varicose veins – visible and palpable, associated with symptoms and possible serious complications, covered by insurances, progressive course unless treated. If present together with spider veins, always to be treated first, before spider therapy
References
Varicose Veins and Spider Veins, Frequently Asked Questions. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Office on Women’s Health. http:/www.womenshealth.gov.
Mayo Clinic. Varicose Veins Overview. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/varicose-veins/home/ovc-20178078 (updated 1/22/2016, accessed 11/30/2016)
Wittens, C., et al., Editor’s Choice – Management of Chronic Venous Disease, Clinical Practice Guidelines of the European Society for Vascular Surgery. Eur J VascEndovasc Surg, 2015. 49: p. 678-737. http://www.ejves.com/article/S1078-5884(15