Atrial Fibrillation
Case Patient
78-year-old patient with H/O Atrial fibrillation, Hypertension, Diabetes, Heart Failure, Coronary Artery disease, Aortic Stenosis was scheduled for Elective Aortic Valve Replacement surgery. Coumadin was advised to be stopped 7 days Prior to Surgery at major university Hospital. Patient was admitted with acute stroke a day prior to his Aortic Valve replacement surgery at Hospital. Had two more episodes of stroke over 24 hrs. period. Patient had permanent aphasia and left hemiparesis and was not considered candidate for Surgery.
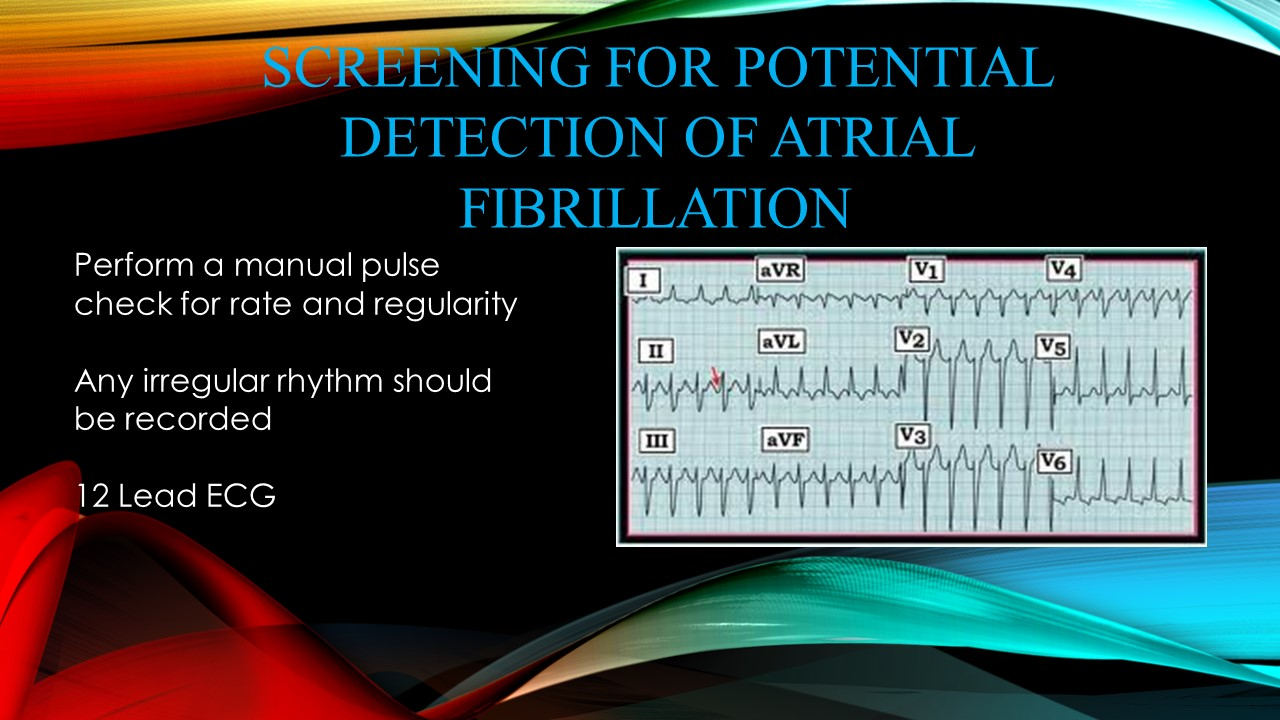
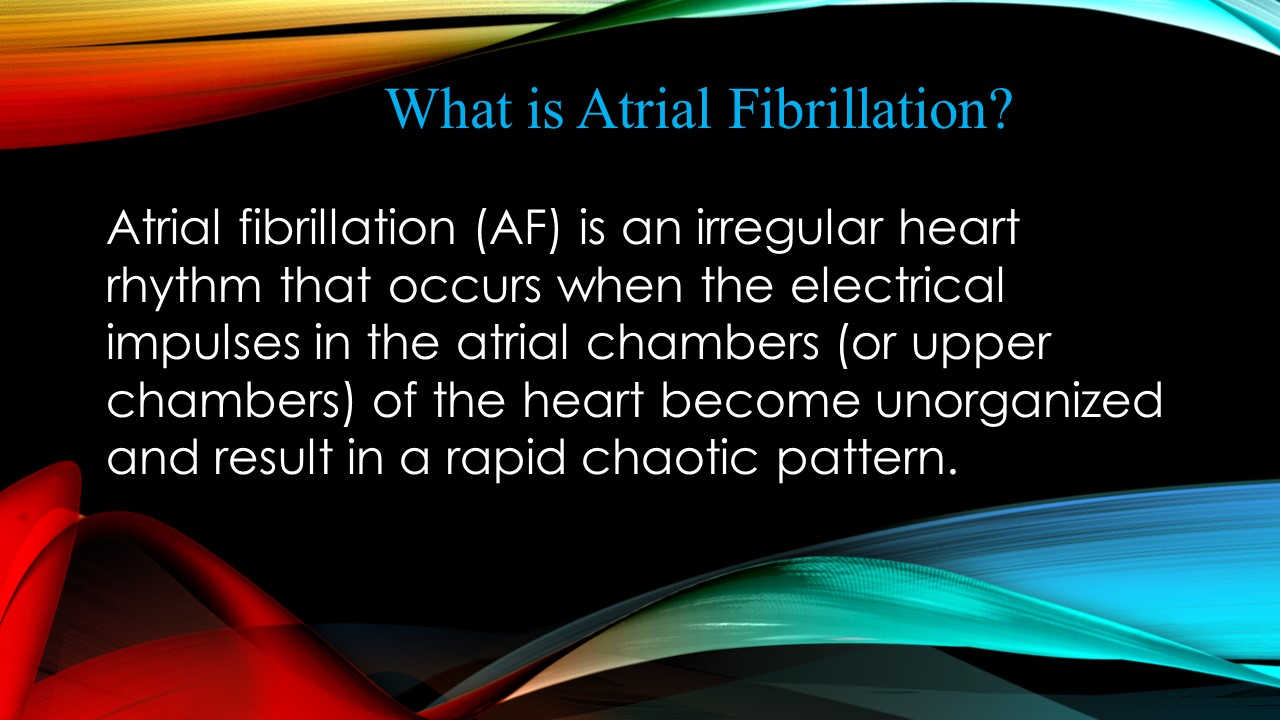
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
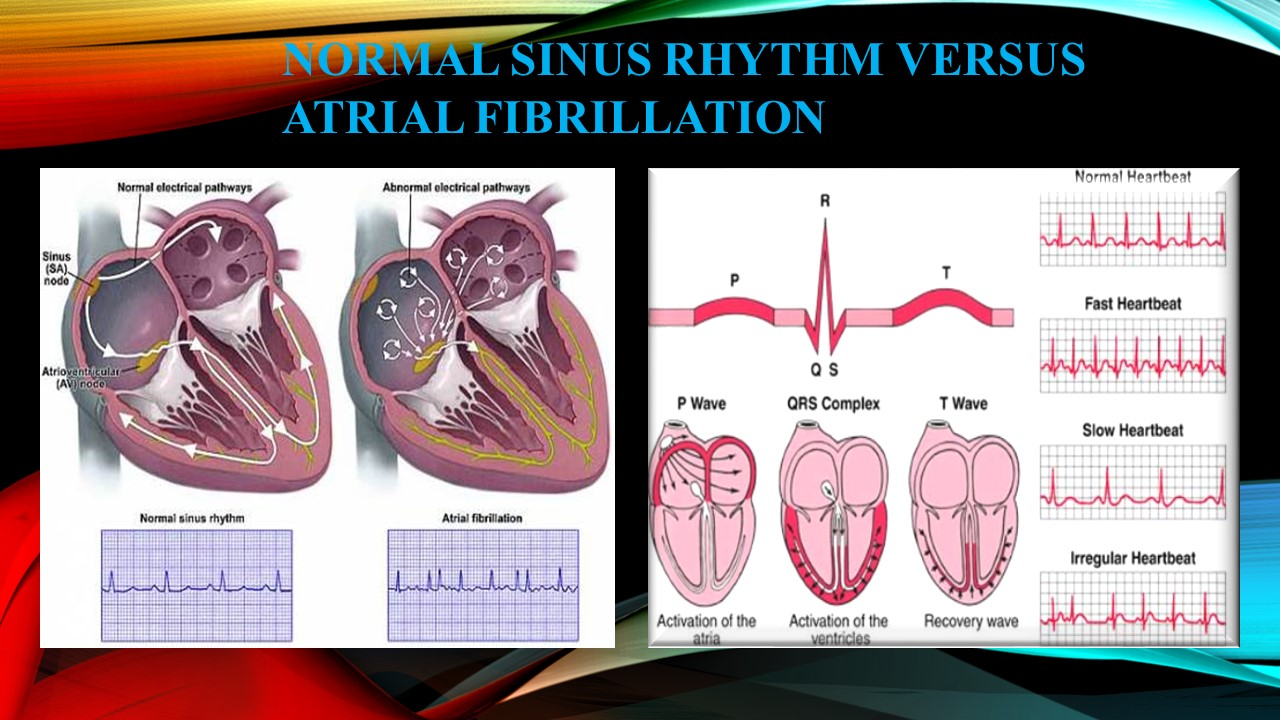
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an irregular heart rhythm that occurs when the electrical impulses in the atrial chambers (or upper chambers) of the heart become unorganized and result in a rapid chaotic pattern.
Clinical Symptoms
No symptoms, Shortness of Breath, Palpitations, Lightheadedness / Presyncope / Syncope Fatigue, Confusion, Sweating
Precipitating Factors
Stimulants (coffee, tea, tobacco, alcohol, illicit drugs) Drugs (inhaled bronchodilators, antidepressants, thyroxin, and response to anti-arrhythmic drugs) Exercise Stress and/or anxiety Recent illness, Hyperthyroidism
Classifications of Atrial Fibrillation
Persistent Atrial Fibrillation, Paroxysmal Arial Fibrillation, Permanent (chronic) Atrial fibrillation
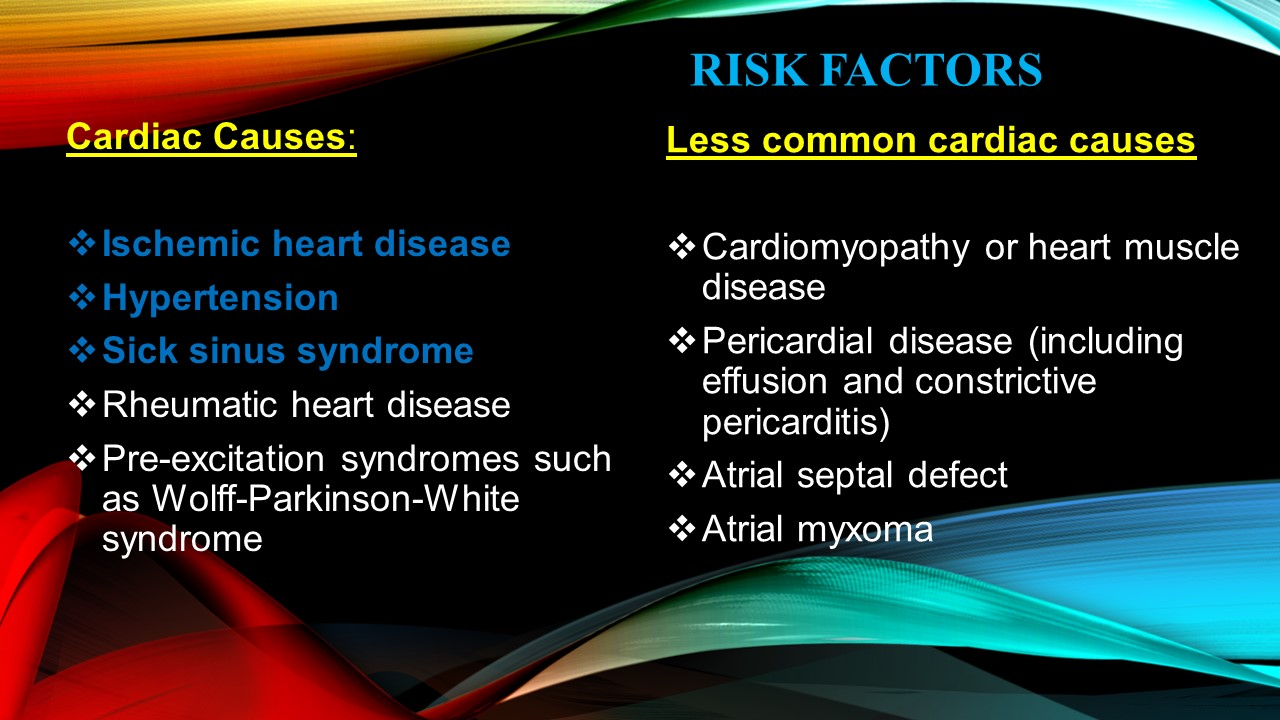
Cardiac Causes:
Ischemic heart disease, Hypertension, Sick sinus syndrome, Rheumatic heart disease, Pre-excitation syndromes such as Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Less common cardiac causes
Cardiomyopathy or heart muscle disease, Pericardial disease (including effusion and constrictive pericarditis), Atrial septal defect, Atrial myxoma.
Non-Cardiac Causes of AF
Acute infections, especially pneumonia, Thyrotoxicosis, Excessive alcohol consumption, Chronic lung disease, Pleural effusions, Pulmonary embolism, Electrolyte depletion
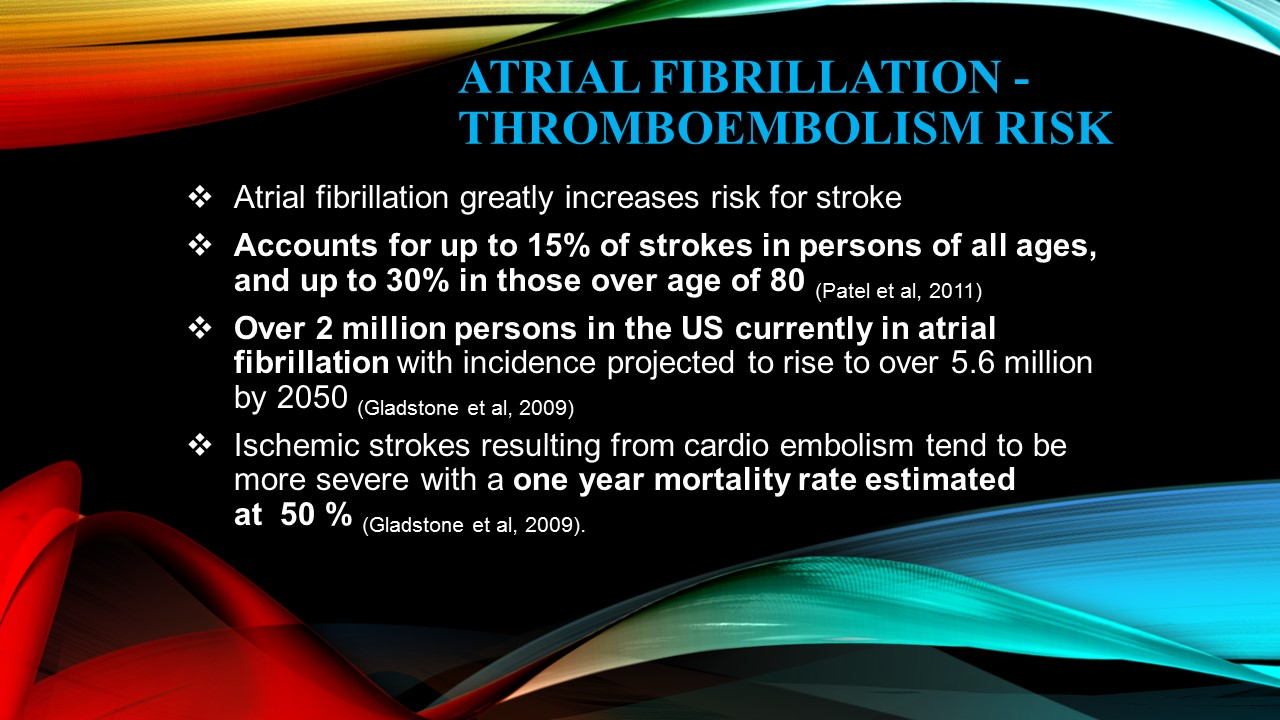
WHY ATRIAL FIBRILLATION CAN BE A DEADLY DISEASE…
AF results in decreased contractility or pumping action of the upper or atrial chambers of the heart This decreased pumping action causes blood to become stagnant and prone to clotting, clot may then travel out of the heart and up to the brain causing STROKE-PARALYSIS.
Other Sequel:
Tachycardia Cardiomyopathy, Limb Ischemia, Bowel Ischemia, Gangrene of Toe/Fingers
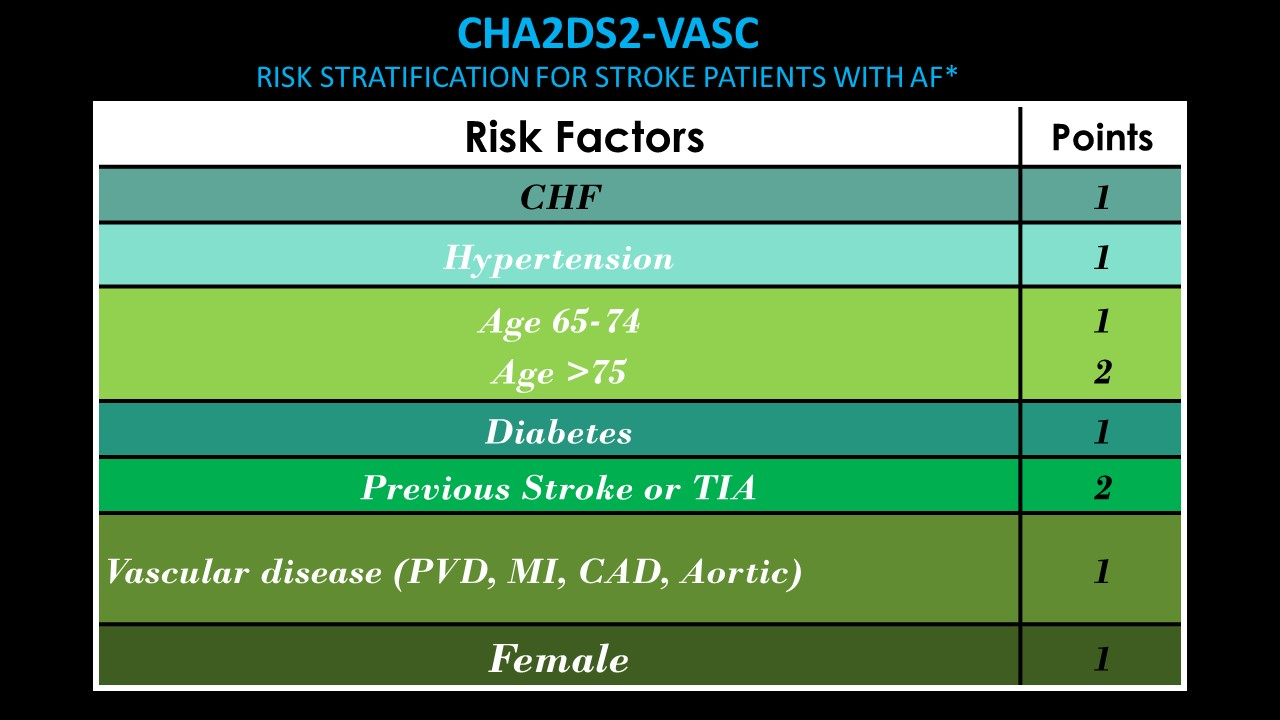
Tools to assist in determining thromboembolism risk in patients with atrial fibrillation and bleeding – CHA2DS2VASc. Score of 2 or more should have systemic anticoagulation.
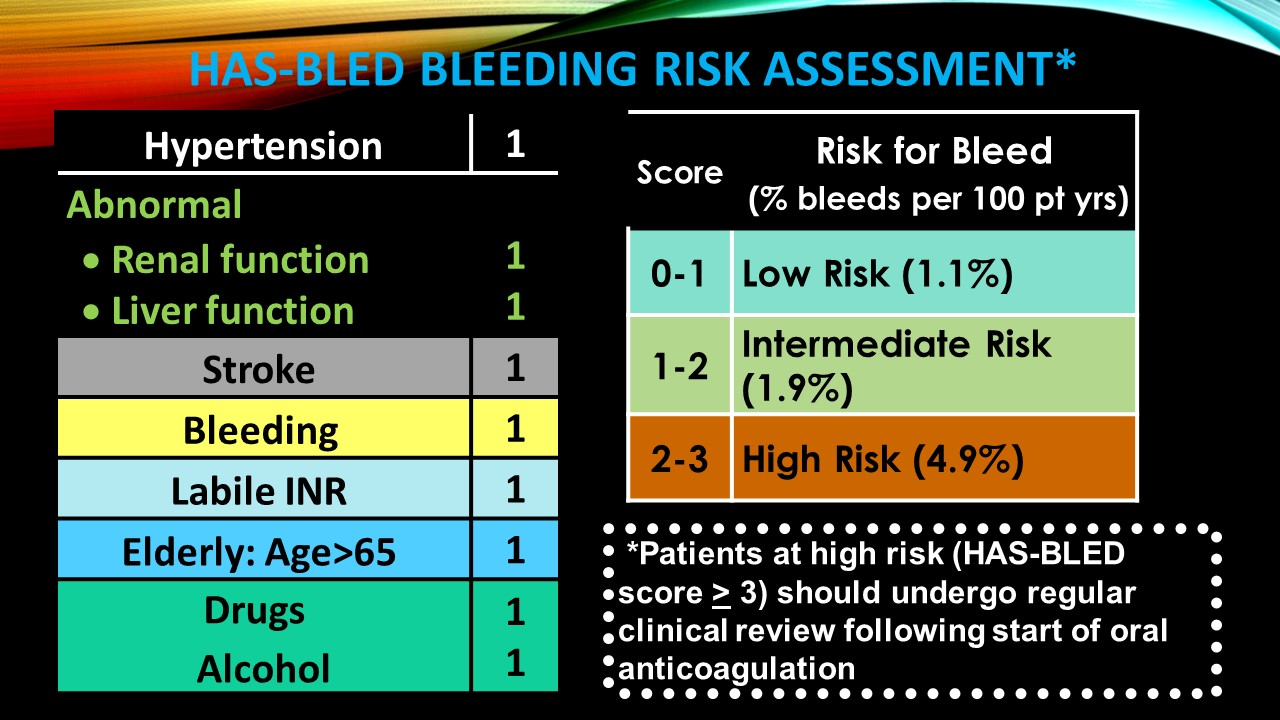
“HASBLED” Assists in measuring a patient’s risk of bleeding if anti coagulated
“Our Prime Purpose in life is to help others and if you can’t help them, at least don’t hurt them.”- Dalai Lama
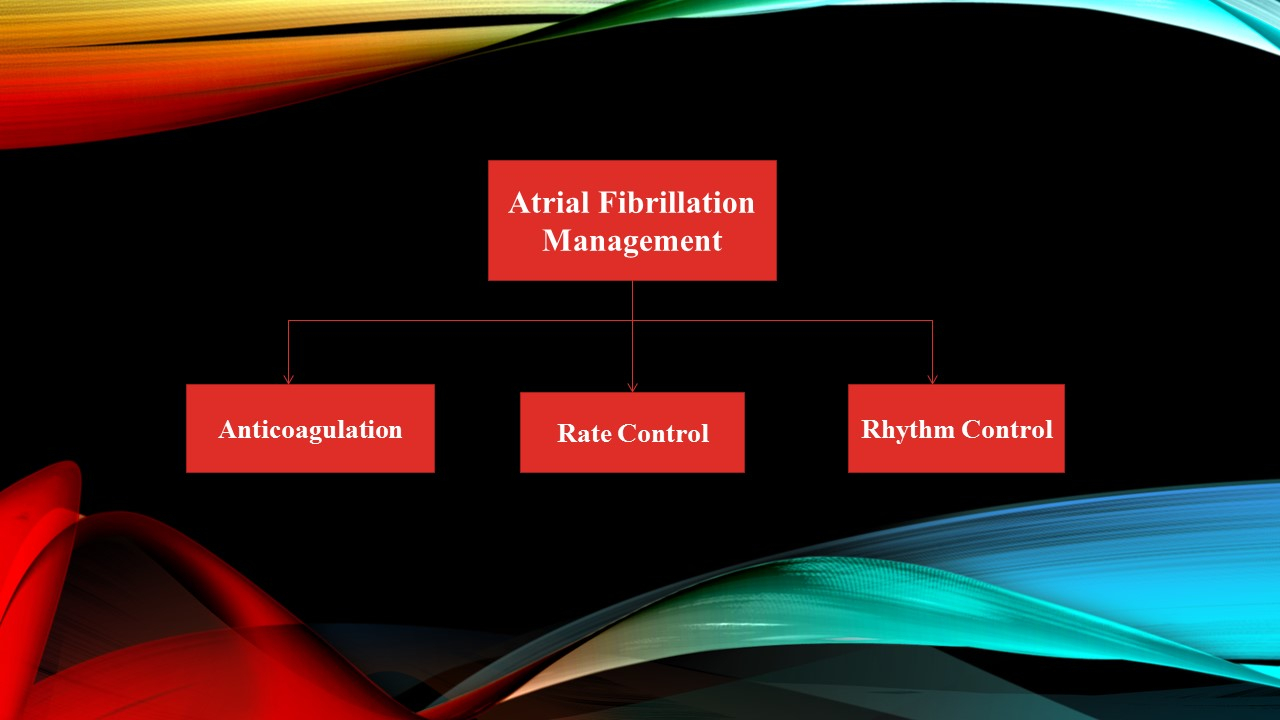
Oral Anticoagulation for Thromboembolism Prevention
Warfarin (Coumadin) – Vitamin K antagonist
Pradaxa (Dabigatran) – Direct thrombin inhibitor, Rivaroxaban (Xarelto) – Factor Xa Inhibitor, Apixaban (Eliquis) – Factor Xa Inhibitor
“Bridging” of anticoagulation refers to administering a shorter acting anticoagulant such as Lovenox when anticoagulation is temporarily stopped. Decision whether a patient needs to stop anticoagulation in order for a procedure to be performed needs to be made by physician and discussed with patient.
Medications used for rate control
Metoprolol, Verapamil, Cardizem, Digoxin
Management of Atrial Fibrillation Rhythm Control
Sotalol/Dofetilide, Amiodarone/Dronedarone, Flecainide (Tambocor) & Propafenone (NO structural heart disease)
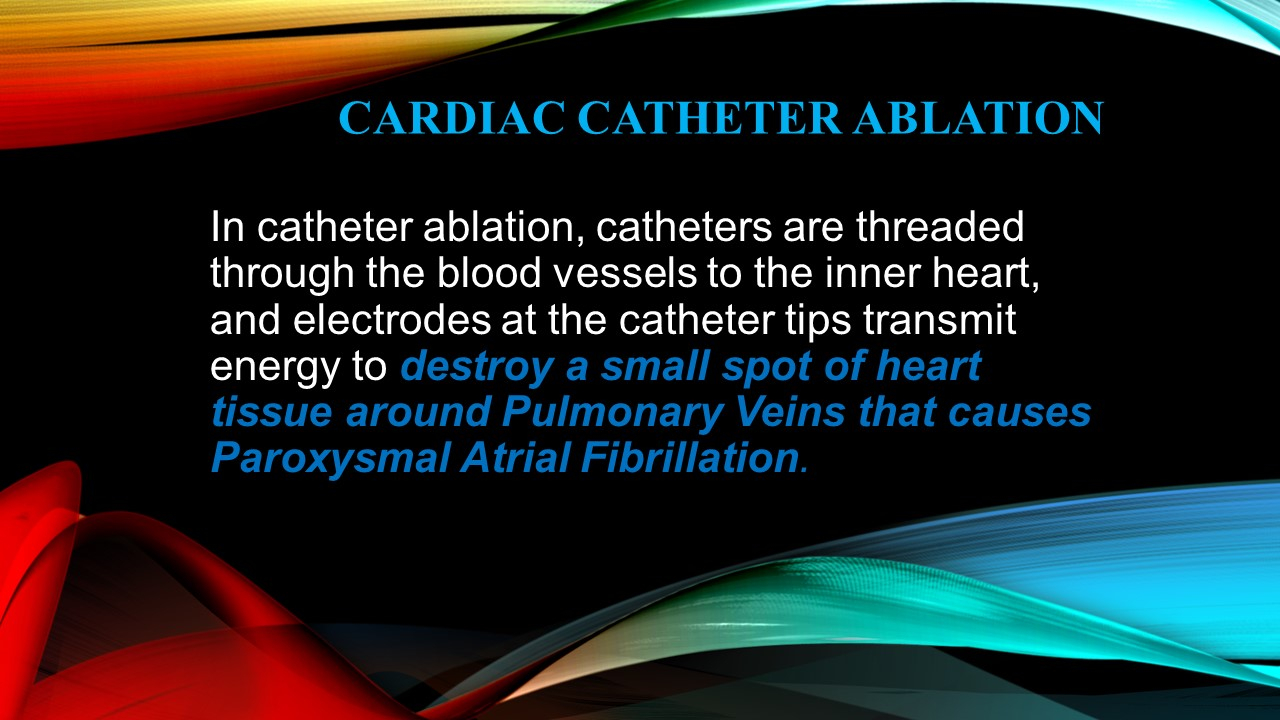
CARDIAC CATHETER ABLATION
In catheter ablation, catheters are threaded through the blood vessels to the inner heart, and electrodes at the catheter tips transmit energy to destroy a small spot of heart tissue around Pulmonary Veins that causes Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation.
It Is OK to Ask Your Doctor
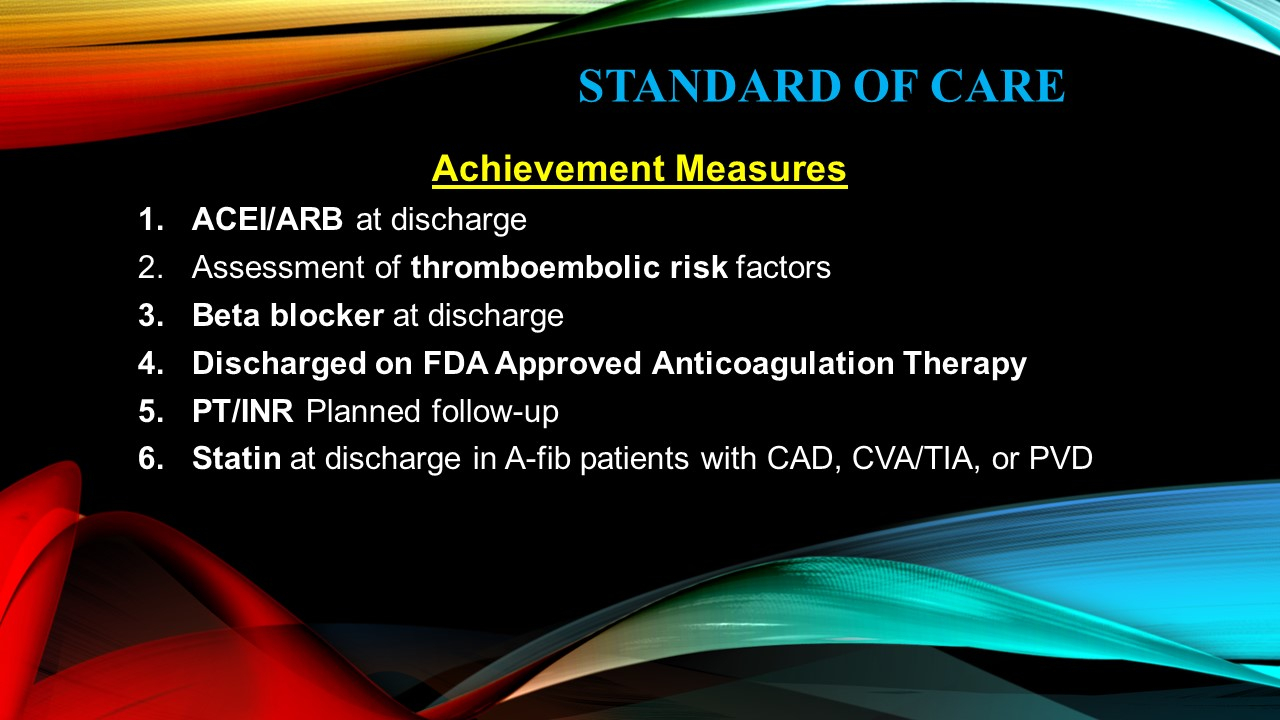
Achievement Measures
- ACEI/ARB at discharge
- Assessment of thromboembolic risk factors
- Beta blocker at discharge
- Discharged on FDA Approved Anticoagulation Therapy
- PT/INR Planned follow-up
- Statin at discharge in A-fib patients with CAD, CVA/TIA, or PVD
Quality
- Aldosterone antagonist at discharge
- Anticoagulation therapy education
- Atrial fibrillation education
- CHA2DS2-VASc score is reported
- Discharge heart rate < 110/bpm
- Smoking cessation
- Warfarin at discharge for valvular atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter patients.